Diferencia entre revisiones de «Código Acelerómetro para Codewarrior 10.6»
(→KBI) |
(→KBI) |
||
| Línea 50: | Línea 50: | ||
[[Archivo:Kbi1.jpg]] | [[Archivo:Kbi1.jpg]] | ||
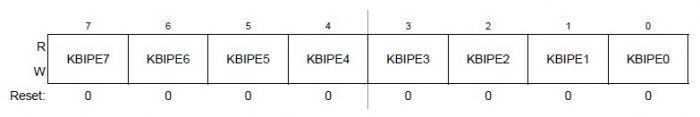
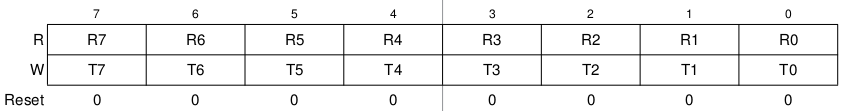
| − | El registro KBIxPE es un registro que está relacionado con los pines de la tarjeta de desarrollo. Nos permite configurar cuáles pines se | + | El registro KBIxPE es un registro que está relacionado con los pines de la tarjeta de desarrollo. Nos permite configurar cuáles pines se habilitarán para las interrupciones. |
[[Archivo:Kbi2.jpg]] | [[Archivo:Kbi2.jpg]] | ||
Revisión del 18:51 22 jun 2016
Contenido
Descripción general
Descripción de funciones
Inicialización de periféricos
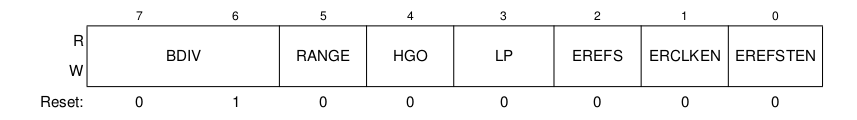
ICS
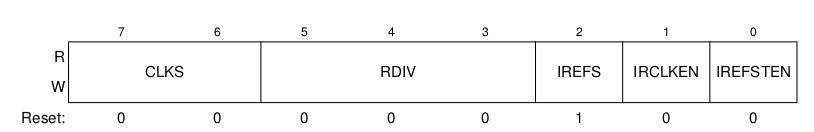
El módulo ICS (Internal Clock Source) maneja las diferentes opciones para la fuente de reloj. Tiene siete modos de operación: FEI, FEE, FBI, FBILP, FBE, FBELP, y stop. En este caso se trabajará con el modo por defecto FEI.
Para inicilizar el ICS deben modificarse tres de sus registros:
ICSC1: ICS Control Register 1
ICSC2: ICS Control Register 2
ICSSC: ICS Status and Control
Rutina de inicialización
#define ICSC1_FEI 0x04
#define ICSC2_FEI 0x06
#define ICSSC_FEI 0x80
void ICS_FEI(void) {
if (NVICSTRM != 0xFF)
ICSTRM = NVICSTRM;
else
ICSTRM = 0xAD;
ICSC1 = ICSC1_FEI;
ICSC2 = ICSC2_FEI;
ICSSC = ICSSC_FEI;
while (ICSC1_CLKS != ICSSC_CLKST) {}
}
KBI
Es el módulo de interrupción por teclado.
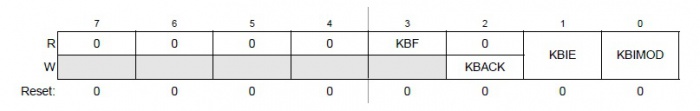
El registro KBIxSC es un registro de estado y control.Está compuesto por 8 bits, de los cuales, los primeros 4 bits tienen un significado específico y permiten habilitar y deshabilitar distintas instancias de las interrupciones y manejar el control del registro.
El registro KBIxPE es un registro que está relacionado con los pines de la tarjeta de desarrollo. Nos permite configurar cuáles pines se habilitarán para las interrupciones.
Rutina de Inicialización
#define KBI_SW KBI1PE_KBIPE2_MASK | KBI1PE_KBIPE3_MASK
void InitKBI(void) {
// Enable KBI1P[3:2] as interrupt
KBI1PE = KBI_SW;
KBI1SC = 0b00000110;
/* ||||
|||+---- KBIMOD = KBI detection mode: 0=edge only
||+----- KBIE = KBI int enable: 1=enabled
|+------ KBACK = KBI int acknowledge: 1=clr IRQF
+------- KBF = KBI flag
*/
}
SCI
void InitSCI(word baud) {
SCI1BD = baud; // set baud
}
ICC
void IIC_configuration (void) {
IIC2F = 0x90;
IIC2C1 = 0xC0;
}
Funciones para la transmisión y recepción de datos
La función RecChar obtiene uno a unos los caracteres enviados a tráves del protocolo IIC desde el registro SCI1D. De igual forma, las funciones SendChar y SendMsg utilizan este registro, descomponen en caracteres el mensaje y lo envían uno a uno.
Los registros utilizados por estas funciones son:
SCIxC2: SCI Control Register 2
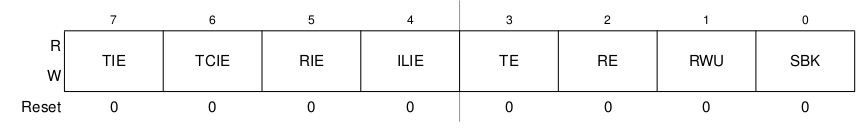 SCIxS1: SCI Status Register 1
SCIxS1: SCI Status Register 1
Recibir caracter
char RecChar(void) {
byte rec_char;
if (SCI1S1_RDRF) // Si el buffer de transmisión esta lleno
rec_char = SCI1D; // Limpio el buffer
SCI1C2_RE = 1; //Habilito la transmisión
while(!SCI1S1_RDRF){ };// Espero hasta que el buffer no esté vacío
rec_char = SCI1D; // Obtengo el caracter enviado
SendChar((char) rec_char);// Reenvío el caracter
return (char) SCI1D;
}
Enviar caracter
void SendChar(char s_char) {
SCI1C2 = 0x08; // enable Tx
while(!SCI1S1_TDRE){ }
SCI1D = (byte) s_char; // 2nd half of TDRE clear procedure
} //end SendChar
}
Enviar mensaje
void SendMsg(char msg[]) {
byte i=0;
char nxt_char;
SCI1C2 = 0x08; // enable Tx
nxt_char = msg[i++];
while(nxt_char != 0x00) {
while(!SCI1S1_TDRE){}
SCI1D = (byte) nxt_char; // 2nd half of TDRE clear procedure
nxt_char = msg[i++];
} //end while((SCI1D
} //end SendMsg
Conversión de datos
Hexadecimal a BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal)
word hex2bcd(word hex){
byte dec[4],i;
word bcd;
for (i=0;i<4;i++){
dec[i] = (byte) (hex%10);
hex = (word) (hex/10);
}
if (hex>0){
bcd=0xffff;
}else{
bcd=(word)((word)(dec[3]<<12) + (word)(dec[2]<<8) + (dec[1]<<4) + dec[0]);
}
return bcd;
}
De ASCII a un byte
byte asc2byte(char n_asc) {
byte n;
n = (byte)(n_asc - 0x30); //Conviere de ASCII a int
if(n > 0x09) // if num is $a or larger...
n -= 0x07; // ...sub $7 to correct
if(n > 0x0f) // if lower case was used...
n -= 0x20; // ...sub $20 to correct
if(n > 0x0f) // if non-numeric character...
n = 0x00; // ...default to '0'
return n;
}
De ASCII a una palabra
word asc2word(byte n_asc[2]) {
word n,n2;
// assumes n_asc[0] is MSB, n_asc[1] is LSB
n = (word)(n_asc[0] - 0x30); //convert from ascii to int
if(n > 0x09) // if num is $a or larger...
n -= 0x07; // ...sub $7 to correct
if(n > 0x0f) // if lower case was used...
n -= 0x20; // ...sub $20 to correct
if(n > 0x0f) // if non-numeric character...
n = 0x00; // ...default to '0'
n = (word)(n<<8); // shift into high byte
n2 = (word)(n_asc[1] - 0x30); //convert from ascii to int
if(n2 > 0x09) // if num is $a or larger...
n2 -= 0x07; // ...sub $7 to correct
if(n2 > 0x0f) // if lower case was used...
n2 -= 0x20; // ...sub $20 to correct
if(n2 > 0x0f) // if non-numeric character...
n2 = 0x00; // ...default to '0'
n += n2; //
return n;
}
char * byte2asc(byte num, byte base) {
byte n;
if (base){
n=(byte)(hex2bcd(num));
}else{
n=num;
} //end if (base)
n_str[0] = (byte)((n>>0x04)+0x30); // convert MSN to ascii
if(n_str[0]>0x39) // if MSN is $a or larger...
n_str[0]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[1] = (byte)((n&0x0f)+0x30); // convert LSN to ascii
if(n_str[1]>0x39) // if LSN is $a or larger...
n_str[1]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[2] = 0x00; // add line feed
return (char *) n_str;
} //end byte2asc
char * word2asc(word num, byte base) {
word n;
if (base){
n=hex2bcd(num);
}else{
n=num;
} //end if (base)
n_str[0] = (byte)((n>>12)+0x30); // convert MSN to ascii
if(n_str[0]>0x39) // if MSN is $a or larger...
n_str[0]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[1] = (byte)(((n>>8)&0x0f)+0x30); // convert 2nd MSN to ascii
if(n_str[1]>0x39) // if LSN is $a or larger...
n_str[1]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[2] = (byte)(((n>>4)&0x0f)+0x30); // convert 2nd MSN to ascii
if(n_str[2]>0x39) // if LSN is $a or larger...
n_str[2]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[3] = (byte)((n&0x0f)+0x30); // convert 2nd MSN to ascii
if(n_str[3]>0x39) // if LSN is $a or larger...
n_str[3]+=0x07; // ...add $7 to correct
n_str[4] = 0x00; // add line feed
return (char *) n_str;
} //end word2asc
Aceleración
void ReadAcceleration(void){
byte i;
signed int temp;
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
temp = IIC_Rec_Data[i] & 0x3F;
if(IIC_Rec_Data[i] & 0x20){
temp |= 0xFFC0;
temp += 32;
IIC_Converted_Data[i] = temp;
}else{
IIC_Converted_Data[i] = temp + 32;
}
}
}
void ShowAcceleration (void)
{
word SampleCNT;
byte j,k;
ReadAcceleration();
ADCSC1 = 0x01;
x.reading[samp] = (dword)( IIC_Converted_Data[0] <<8);
ADCSC1 = 0x08;
y.reading[samp] = (dword)( IIC_Converted_Data[1] <<8);
ADCSC1 = 0x09;
z.reading[samp] = (dword)( IIC_Converted_Data[2] <<8);
StartTPM(0); //0 = TPM prescaler = /2
if(samp>0){
switch (mode){
case filter: filter_data(); break;
case avg : avg_data(); break;
default : copy_data();
}
} else {
copy_data();
}
SampleCNT = StopTPM();
if (SampleCNT<0x0100) {
for(j=0xff;j>0;j--){
for(k=0x10;k>0;k--){}
}
}
// Display Acceleration
SendMsg("\r\n");
SendMsg(word2asc((word)x.result[samp],dis_base));
SendMsg(",");
SendMsg(word2asc((word)y.result[samp],dis_base));
SendMsg(",");
SendMsg(word2asc((word)z.result[samp],dis_base));
SendMsg(",");
SendMsg(word2asc(SampleCNT,dis_base));
// Shift array of results if we hit max
if (samp >= max-1) {
for (j=0;j<max-1;j++){
x.result[j] = x.result[j+1];
x.reading[j] = x.reading[j+1];
y.result[j] = y.result[j+1];
y.reading[j] = y.reading[j+1];
z.result[j] = z.result[j+1];
z.reading[j] = z.reading[j+1];
}
samp = max-1;
} else {
samp++;
} //end if (i => max)
}
Funciones del Maestro
void Master_Read_and_Store(void) {
IIC_Rec_Data[rec_count++] = IIC2D;
}
void Master_Write_MMA7660_register(byte transbytes) {
last_byte = 0; // Initialize variables to 0
count = 0;
bytes_to_trans = transbytes;
if (transbytes == 0) return;
IIC2C1_TX = 1; // Set TX bit for Address cycle
IIC2C1_MST = 1; // Set Master Bit to generate a Start
IIC2D = mma7660[count++]; // Send first byte (should be 7-bit address + R/W bit)
}
void Master_Read_MMA7660_register(byte transbytes, byte recbytes) {
rec_count = 0; // Initialize variables to 0
last_byte = 0;
count = 0;
repeat_start_sent = 0;
bytes_to_trans = transbytes;
num_to_rec = recbytes;
if (transbytes == 0) return;
IIC2C1_TXAK = 0;
IIC2C1_TX = 1; // Set TX bit for Address cycle
IIC2C1_MST = 1; // Set Master Bit to generate a Start
reading_mma7660_reg = 1;
IIC2D = mma7660[count++]; // Send first byte (should be 7-bit address + R/W bit)
}